Carregando conteúdo…
Oncology
Sources
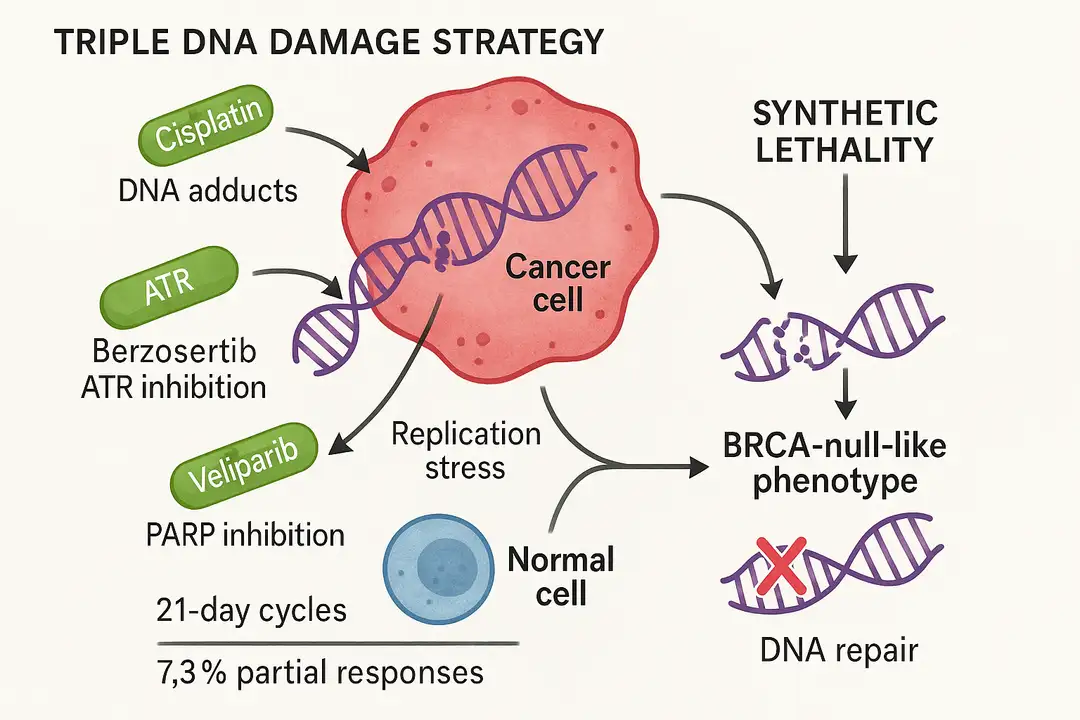
- O'Sullivan Coyne, G., et al. (2025). Safety and Tolerability of Berzosertib, an Ataxia-Telangiectasia Related Inhibitor, and Veliparib, an Oral Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor, in Combination With Cisplatin in Patients With Refractory Solid Tumors. JCO Precision Oncology, 9, e2500055. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO-25-00055.
Highlights
SnackableHealth® |Non-cardiac effects in HELIOS-B trial: gastrointestinal symptoms and quality-of-life signals discussed by Drs. Mike Gibson and Tony Urey
ASCO GU® 2026

Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) Provides Significant Clinical Benefit Over Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), Marking a Potential Shift in the Therapeutic Standard for HER2+ Breast Cancer

SnackableHealth® |Non-cardiac effects in HELIOS-B trial: gastrointestinal symptoms and quality-of-life signals discussed by Drs. Mike Gibson and Tony Urey

ASCO GU® 2026

Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) Provides Significant Clinical Benefit Over Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), Marking a Potential Shift in the Therapeutic Standard for HER2+ Breast Cancer

