Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) Provides Significant Clinical Benefit Over Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), Marking a Potential Shift in the Therapeutic Standard for HER2+ Breast Cancer
Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) Outperforms Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in Patients With High-Risk HER2+ Breast Cancer After Neoadjuvant Therapy

Carregando conteúdo…
ESMO®2025
Oncology
Highlights
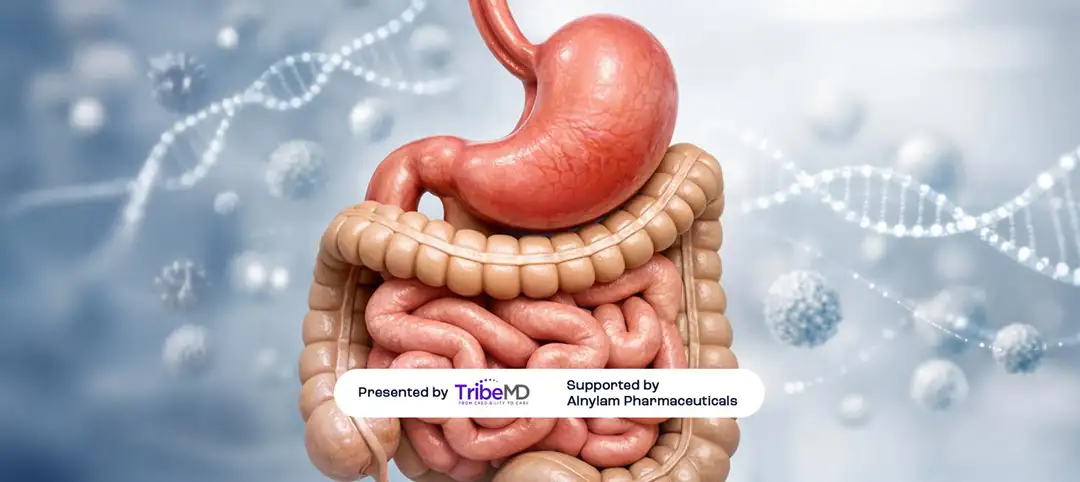
SnackableHealth® |Non-cardiac effects in HELIOS-B trial: gastrointestinal symptoms and quality-of-life signals discussed by Drs. Mike Gibson and Tony Urey
ASCO GU® 2026

Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) Provides Significant Clinical Benefit Over Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), Marking a Potential Shift in the Therapeutic Standard for HER2+ Breast Cancer

SnackableHealth® |Non-cardiac effects in HELIOS-B trial: gastrointestinal symptoms and quality-of-life signals discussed by Drs. Mike Gibson and Tony Urey

ASCO GU® 2026

Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) Provides Significant Clinical Benefit Over Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), Marking a Potential Shift in the Therapeutic Standard for HER2+ Breast Cancer

